Homogenizer Machine: A Complete Guide on
I. Introduction
1.1 What is a homogenizer machine?
A homogenizer machine is a specialized equipment designed to create a homogeneous mixture by reducing the size of particles or droplets within a liquid or semi-solid medium. This process is achieved through the application of intense mechanical forces, such as high pressure, shear, or ultrasonic waves, breaking down the particles and distributing them evenly throughout the medium.
1.2 The importance of homogenizer machines in modern processing industries
In today’s modern processing industries, homogenizer machines play a crucial role in achieving desired product consistency, stability, and quality. Whether it’s in the food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, or biotechnology sectors, these machines are essential for ensuring uniform dispersion and reducing particle size, leading to improved product texture, shelf life, and overall performance.
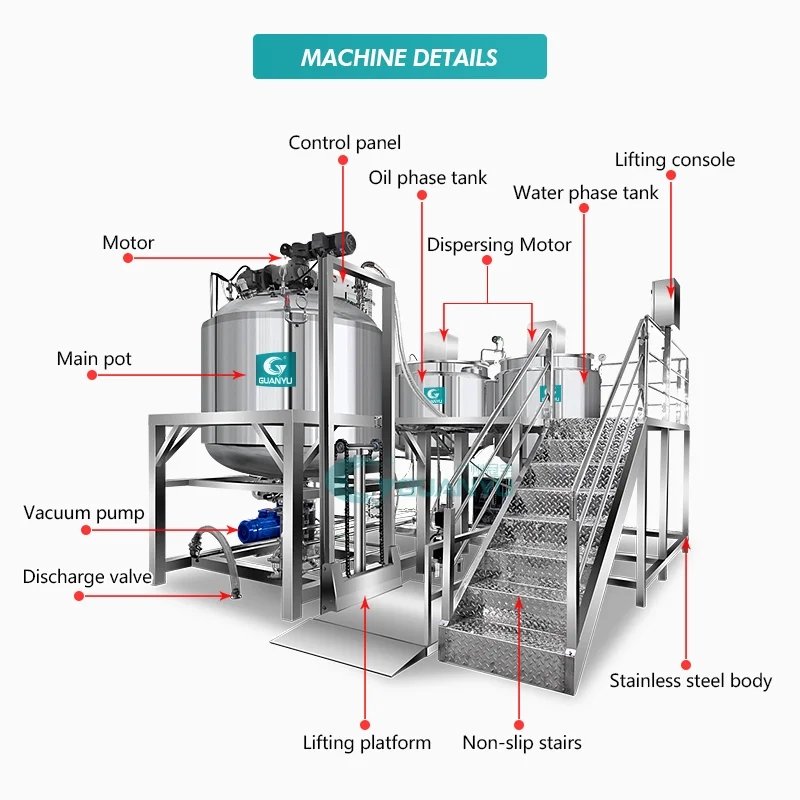
II. Working Principles of Homogenizer Machines
2.1 High-pressure homogenization principle
High-pressure homogenizers work by forcing the product through a narrow gap or valve at extremely high pressures, typically ranging from 10,000 to 30,000 psi. The intense shear forces and cavitation effects cause the particles or droplets to break down into smaller, more uniform sizes.
2.2 Mechanical shear principle
Mechanical shear homogenizers rely on the high-speed rotation of blades or rotors to create intense shear forces within the product. This shearing action disrupts particle agglomerates and reduces their size, resulting in a uniform dispersion.
2.3 Ultrasonic homogenization principle
Ultrasonic homogenizers utilize high-frequency sound waves to create cavitation bubbles within the medium. The collapse of these bubbles generates intense shockwaves and localized high temperatures, leading to the breakdown of particles and droplets.

III. Applications of Homogenizer Machines
3.1 Homogenizers in the Dairy Industry
Homogenizers are essential in dairy processing for producing consistent and stable milk, cream, and other dairy products. They ensure even distribution of milk fat globules, preventing separation and extending shelf life. This homogenization process is crucial for achieving the desired texture, mouthfeel, and stability in dairy products.
3.2 Homogenizers in the Cosmetics and Personal Care Industry
In the cosmetics industry, homogenizers are used to create emulsions, dispersions, and suspensions for various products, such as creams, lotions, and makeup. They contribute to desirable textures and improved product stability. Homogenizers play a vital role in developing cosmetic formulations with a smooth, homogeneous appearance and prolonged shelf life.
3.3 Homogenizers in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies rely on homogenizers to produce uniform dispersions of active ingredients in drug formulations, ensuring consistent dosing and bioavailability. Precise particle size reduction and even distribution of active compounds are critical for effective drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy.
3.4 Homogenizers in the Food Processing Industry
Homogenizers are widely used in the food industry for creating stable emulsions, dispersions, and suspensions in products like salad dressings, mayonnaise, sauces, and beverages. They help achieve desired textures, mouthfeel, and extended shelf life. Homogenization is essential for maintaining the quality and consistency of various food products.
3.5 Homogenizers in the Biotechnology Industry
In biotechnology applications, homogenizers are used for cell disruption, protein extraction, and the production of liposomes and nanoparticles for various research and industrial purposes. Precise control over particle size and distribution is crucial in biotechnology processes, making homogenizers invaluable tools.
IV. Major Types of Homogenizer Machines
4.1 High-Pressure Homogenizers
These homogenizers use extremely high pressures to force the product through a narrow gap or valve, achieving particle size reduction and uniform dispersion.
4.2 Ultra-High-Pressure Homogenizers
Ultra-high-pressure homogenizers operate at even higher pressures, typically above 30,000 psi, and are suitable for processing highly viscous or challenging materials.
4.3 In-Line Homogenizers
In-line homogenizers are designed for continuous processing, allowing the product to flow through the homogenizing valve or chamber without interruption.
4.4 Immersion Homogenizers
Immersion homogenizers, also known as rotor-stator homogenizers, feature a shaft with a rotor that is immersed directly into the product, creating high shear forces for localized homogenization.
4.5 Laboratory Homogenizers
Laboratory homogenizers are smaller-scale versions designed for research and development purposes, enabling the testing and optimization of formulations before scaling up to production.
V. Key Factors in Selecting the Right Homogenizer Machine
5.1 Processing Capacity
The required throughput and batch size should be carefully considered when selecting a homogenizer machine to ensure efficient and cost-effective operation.
5.2 Required Degree of Homogenization
Different applications may require varying degrees of particle size reduction and uniformity, influencing the choice of homogenizer type and operating parameters.
5.3 Viscosity of the Medium
The viscosity of the product being processed can impact the homogenization efficiency and the required pressure or shear forces.
5.4 Sanitary Requirements
Industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics have strict hygiene standards, necessitating the selection of homogenizers with appropriate sanitary designs and ease of cleaning.
5.5 Budget
Homogenizer machines can vary significantly in cost, depending on their size, capacity, and advanced features. Balancing performance requirements with budget constraints is crucial.
5.6 Guanyu Machinery Company
Established in 1987, Guanyu Machinery Company is a leading manufacturer of homogenizer machines and other processing equipment for the foodstuff, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries. With advanced technology, production, and inspection capabilities, as well as specialized processes, they provide a wide range of equipment tailored to market requirements, ensuring high-quality solutions for their customers.
Conclusion:
Homogenizer machines are versatile and indispensable tools in various industries, enabling the production of consistent, stable, and high-quality products. By understanding their working principles, applications, and types, manufacturers can make informed decisions in selecting the most suitable homogenizer machine for their specific needs. With the right homogenizer, companies can achieve improved product texture, extended shelf life, and enhanced overall performance, while meeting stringent quality and regulatory standards. As technology continues to evolve, homogenizer machines will likely become even more advanced, offering greater efficiency, precision, and customization to meet the ever-changing demands of diverse industries.
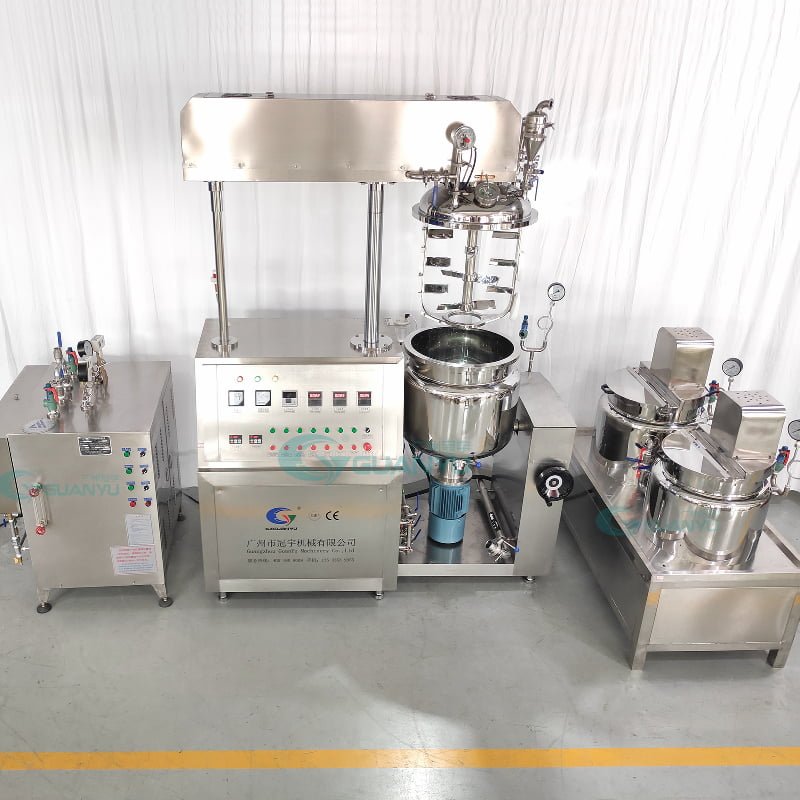
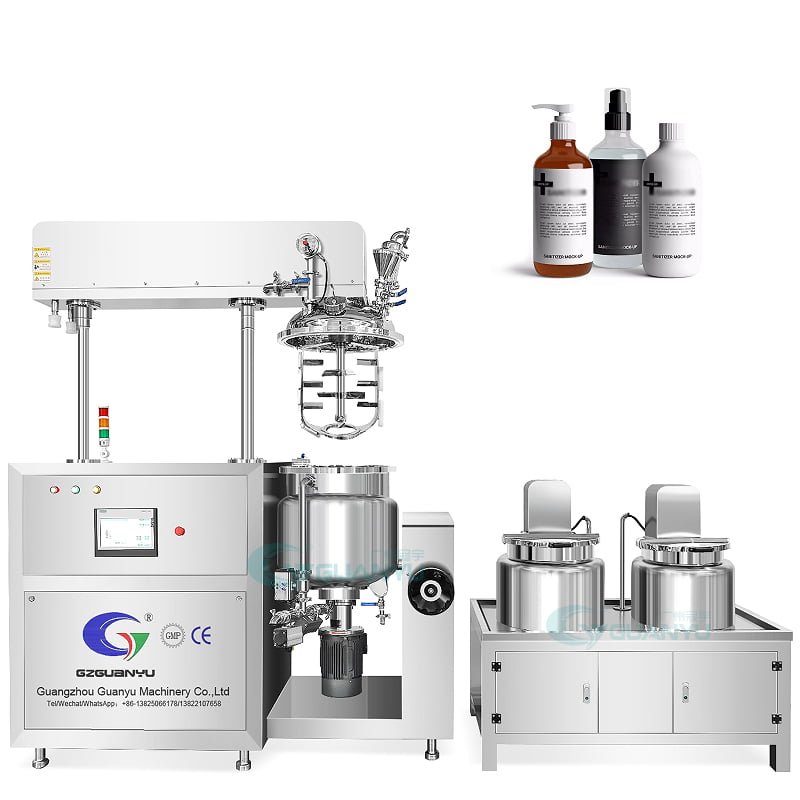
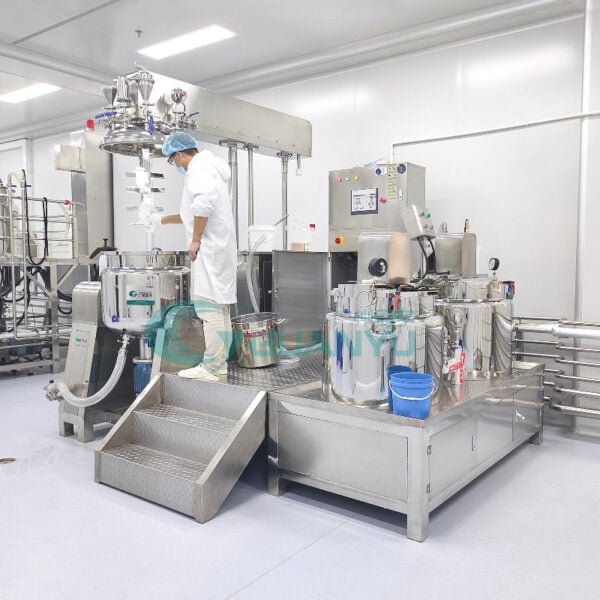



Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.