
Vous êtes confronté à un défi unique lorsque vous essayez de produire de la mayonnaise faible en gras. Retirer la graisse change la texture, goût, et l'apparence que les clients attendent. La graisse aide à garder la mayonnaise stable et crémeuse, donc le réduire peut rendre le produit moins ferme et moins lisse. Pour résoudre ça, vous pouvez utiliser des ingrédients spéciaux comme des hydrocolloïdes pour améliorer l'épaisseur et la stabilité. Avancé, l'équipement personnalisable vous aide également à contrôler chaque étape avec précision. La demande mondiale croissante d’aliments plus sains montre pourquoi vous avez besoin d’un guide technique pour réussir.
Principaux à retenir
Suivez un processus structuré pour produire de la mayonnaise faible en gras. Chaque étape, de la formulation des prémix au refroidissement, est crucial pour obtenir la bonne texture et le bon goût.
Relevez les défis courants tels que la texture et la stabilité en utilisant des substituts de graisse et des hydrocolloïdes. Ces ingrédients aident à maintenir l'onctuosité et à prévenir la séparation.
Investissez dans des équipements avancés tels que des émulsificateurs sous vide et des moniteurs de viscosité en ligne. Ces outils améliorent l'efficacité de la production et garantissent une qualité constante.
Effectuez des tests sensoriels réguliers pour vous assurer que votre mayonnaise répond aux attentes des clients.. Cela inclut la vérification de la texture, saveur, et uniformité des couleurs.
Restez à jour sur les normes réglementaires pour garantir la conformité. Un étiquetage précis et l'approbation des ingrédients sont essentiels pour la sécurité et la confiance des consommateurs..
Aperçu du guide technique
Étapes clés de la production
Vous devez suivre un processus clair lorsque vous préparez une mayonnaise faible en gras. Chaque étape du guide technique vous aide à créer un produit avec la bonne texture et le bon goût. Voici un tableau qui présente les principales étapes tu devrais prendre:
Étape | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Formuler des prémélanges avec des ingrédients secs, cellulose microcristalline, gomme, eau, et du lactosérum ou de l'œuf. |
2 | Broyer la cellulose microcristalline pour obtenir un mélange uniforme. |
3 | Mélanger tous les prémélanges dans une cuve à lisier avec d'autres ingrédients. |
4 | Mélangez la bouillie pendant au moins cinq minutes. |
5 | Cuire la bouillie entre 175°F et 200°F pendant 15 à 75 secondes. |
6 | Refroidir la bouillie cuite à 70°F. |
7 | Broyer à nouveau pour obtenir une texture onctueuse. |
Vous pouvez constater que chaque étape du Guide technique s'appuie sur la précédente. Il faut faire attention à la température et aux temps de mélange. Ces détails vous aident à obtenir une mayonnaise onctueuse et stable.
Principaux défis
Quand on réduit le gras dans la mayonnaise, vous faites face à plusieurs défis. Le Guide technique souligne trois problèmes principaux: texture, stabilité, et la sensation en bouche. Le tableau ci-dessous explique ces défis et comment vous pouvez les résoudre:
Défi | Description | Stratégie pour relever les défis |
|---|---|---|
Texture | Moins de matières grasses rend le produit moins crémeux. | Utilisez des substituts de graisse pour imiter la sensation de graisse. |
Stabilité | Une faible teneur en graisse affaiblit l'émulsion et peut provoquer une séparation. | Essayez les émulsions eau dans huile dans eau. |
Sensation en bouche | La teneur réduite en matières grasses donne une sensation en bouche moins satisfaisante que la mayonnaise ordinaire. | Ajouter des hydrocolloïdes pour améliorer la viscosité. |
Conseil: Vous pouvez améliorer vos résultats en testant différents ingrédients et méthodes de mélange. La bonne approche vous aide à surmonter ces problèmes courants.
En suivant le Guide Technique, vous pouvez relever ces défis et produire une mayonnaise faible en gras de haute qualité.
Ingrédients de la mayonnaise faible en gras

Substituts et substituts de graisse
Vous pouvez utiliser de nombreux ingrédients pour remplacer le gras dans la mayonnaise. Ces substituts vous aident à conserver la texture et le goût crémeux que les gens attendent. Le tableau ci-dessous présente certaines des options les plus efficaces:
Type d'ingrédient | Propriétés | Montant recommandé (en poids) |
|---|---|---|
Amidon de riz non cuit | Propriétés mimétiques des graisses, opacité souhaitée | 1-10% (de préférence 1-7%) |
Graisses comestibles (Par exemple, huile de soja) | Peut être inclus jusqu'à 20% en poids, de préférence 1-15% | 1-15% (si inclus) |
Autres particules non protéiques | Peut remplacer la fécule de riz, comprend de l'amidon non gélatinisé, cellulose | N / A |
Vous pouvez également utiliser des protéines de levure pour améliorer la stabilité et la texture de l'émulsion.. Des études montrent que remplacer 20% à 40% de graisse avec des protéines de levure vous donne une mayonnaise aux propriétés similaires aux versions entières. À 40% remplacement, vous obtenez la plus haute acceptabilité sensorielle et plus 95% stabilité de l'émulsion.
Émulsifiants et stabilisants
Vous avez besoin des bons émulsifiants et stabilisants pour garder votre mayonnaise lisse et stable.. Voici quelques options que vous pouvez utiliser:
Le gluten modifié augmente la stabilité de l'émulsion et améliore les propriétés sensorielles.
Les protéines de lactosérum retardent la coalescence des gouttelettes et améliorent la texture.
Protéines de lactosérum microparticulaires (comme Simplesse™) imite les gouttelettes d'huile pour une sensation en bouche crémeuse.
Choisissez votre émulsifiant en fonction des conditions de traitement, taille des gouttelettes, et la stabilité que vous souhaitez.
Les grosses molécules hydrocolloïdes aident également à empêcher l’huile et l’eau de se séparer. Ils gardent votre mayonnaise épaisse, crémeux, et opaque.
Options d'étiquette propre
Si vous souhaitez créer un produit clean label, tu as plusieurs choix:
Des huiles plus saines, comme l'huile de soja ou d'avocat, peut réduire le mauvais cholestérol.
Antioxydants naturels issus de farines de fruits (comme la nectarine, pomme, ou poire) remplacer les conservateurs et le sucre.
Protéines végétales, comme le lupin et les féveroles, rendez votre mayonnaise adaptée aux végétaliens et aux personnes allergiques.
Les conservateurs naturels aident à garder votre produit frais sans produits chimiques synthétiques.
Les fabricants utilisent désormais de nouveaux ingrédients comme l'aquafaba et les huiles végétales pour améliorer la saveur et la texture. Le Guide technique recommande ces options pour vous aider à répondre à la demande des consommateurs en matière de produits plus sains., produits plus propres.
Stratégies de formulation
Conception d'émulsion
Vous devez concevoir une émulsion stable pour réaliser une mayonnaise allégée qui répond aux attentes des clients. Vous pouvez utiliser des émulsifiants naturels comme le jaune d’œuf et des complexes de polysaccharides pour renforcer les propriétés émulsifiantes.. Méthodes de traitement non thermiques, tels que le traitement à haute pression et les ultrasons de haute intensité, contribuer à préserver ces propriétés. Les stabilisants comme l'amidon d'amarante modifié améliorent la stabilité. Des formulations innovantes, y compris les émulsions à base de jaune d'œuf et de caséine et les oléofousses à base de cire de tournesol, permettent de réduire les graisses tout en gardant la texture. Le tableau ci-dessous montre techniques courantes de conception d'émulsion:
Technique de conception d'émulsion | Description |
|---|---|
Émulsifiants naturels | Utilisez des complexes de jaune d’œuf et de polysaccharides pour améliorer les propriétés émulsifiantes. |
Traitement non thermique | Appliquer une haute pression ou des ultrasons pour préserver la stabilité de l'émulsion. |
Stabilisateurs | Ajoutez de l'amidon d'amarante modifié pour une meilleure stabilité. |
Formulations innovantes | Développer des émulsions à base de jaune-caséine ou de cire de tournesol pour une mayonnaise allégée. |
Pectine et protéines de soja | Solidifier les gouttelettes d'huile dans des gels d'émulsion faibles en gras. |
Auto-assemblage jaune-caséine | Créez une mayonnaise faible en gras avec une texture riche en gras. |
Hydrocolloïdes et épaississants
Les hydrocolloïdes jouent un rôle clé dans une mayonnaise faible en gras. Vous les utilisez pour lier l’eau et émulsionner les ingrédients, ce qui empêche la synérèse et maintient votre produit lisse. Les épaississants aident à imiter la fonction des graisses, afin que vous puissiez réduire la teneur en matières grasses tout en obtenant le volume et la texture souhaités. Le les hydrocolloïdes les plus courants comprennent:
Gomme xanthane (du métabolisme microbien)
gomme de guar (à partir de graines de plantes)
Gomme arabique (de la sécrétion des arbres)
Pectine (à partir d'écorces de fruits)
Gélatine (à partir de colloïdes animaux)
Carraghénane (à partir d'algues)
Alginates (à partir d'algues)
Dérivés cellulosiques
Amidon modifié
Vous pouvez voir comment différents hydrocolloïdes affectent la stabilité et la viscosité le tableau ci-dessous:
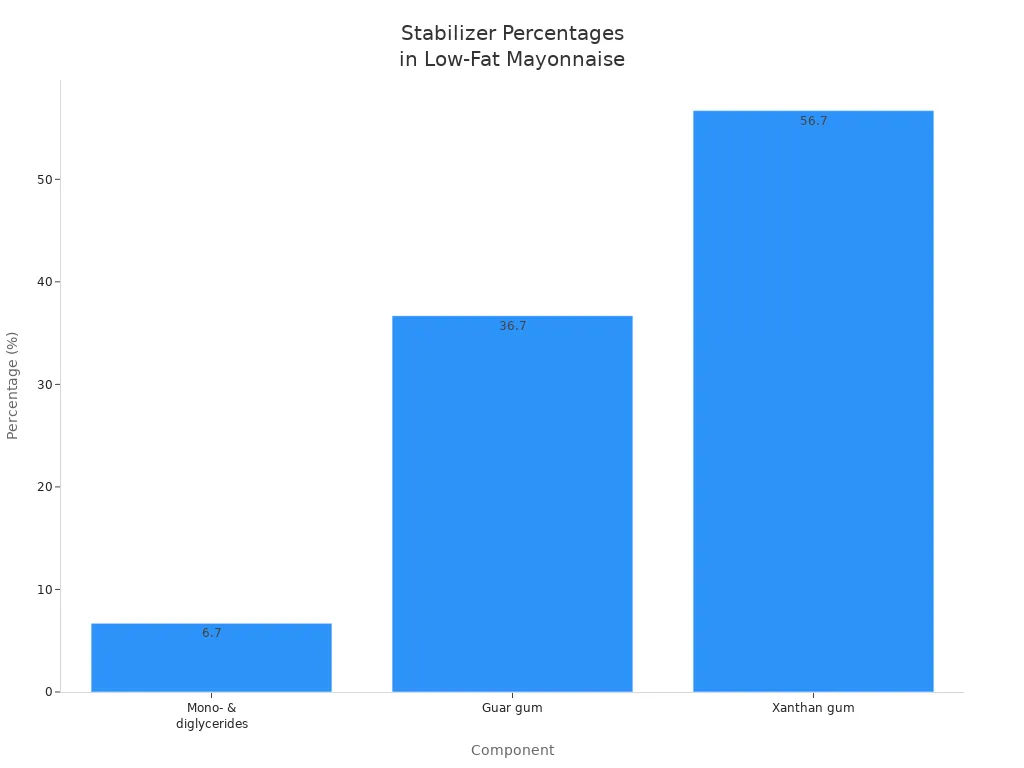
Composant | Pourcentage | Effet sur les propriétés |
|---|---|---|
Mono- & diglycérides | 6.7% | Contribue à la stabilité et à la texture de l'émulsion. |
gomme de guar | 36.7% | Améliore la viscosité et la stabilité de l'émulsion. |
Gomme xanthane | 56.7% | Impact le plus significatif sur la stabilité, viscosité, et l'acceptation. |
Conseil: Vous pouvez ajuster le type et la quantité d'hydrocolloïde en fonction de la texture souhaitée.
Optimisation de la saveur et de la texture
Vous pouvez optimiser la saveur et la texture en choisissant les bons substituts de protéines et de graisses.. Le lait de soja fonctionne comme une source de protéines et peut remplacer le jaune d'oeuf, vous donnant de bonnes propriétés émulsifiantes. Quand vous combinez du lait de soja avec du mono- et diglycérides, vous créez une mayonnaise faible en gras de haute qualité. Amidon modifié, inuline, et les protéines aident à stabiliser l'émulsion et à augmenter la viscosité. Les graisses ajoutent de la saveur, texture, et durée de conservation, vous devez donc sélectionner des substituts qui imitent ces qualités. Le Guide technique recommande de tester différentes combinaisons pour trouver le meilleur résultat pour votre produit.
Processus et équipement de production

Techniques d'émulsification
Vous devez créer une émulsion stable pour faire une mayonnaise faible en gras. Le processus de mélange est très important. Vous devez mélanger l'huile, eau, et les stabilisateurs avec soin. Cela vous aide à éviter la séparation et à garder votre mayonnaise onctueuse.. Vous utilisez souvent des ingrédients stabilisants supplémentaires dans les recettes faibles en gras. Le type d'huile que vous choisissez peut affecter la facilité avec laquelle votre mayonnaise se gâte en raison de l'oxydation..
Les techniques modernes d'émulsification vous aident à améliorer la stabilité et la texture. Vous pouvez utiliser des protéines de microalgues, tel que Dunaliella saline, pour booster les propriétés émulsifiantes. L'extraction assistée par ultrasons vous aide à obtenir plus de protéines à partir des ingrédients, qui améliore la viscosité et les qualités sensorielles. Le tableau ci-dessous présente certaines des dernières avancées:
Avancement | Description |
|---|---|
Utilisation de protéines de microalgues | La protéine Dunaliella salina augmente la stabilité et les propriétés émulsifiantes. |
Extraction assistée par ultrasons | Améliore l'extraction des protéines pour une meilleure texture et des propriétés antioxydantes. |
Propriétés fonctionnelles | Les protéines améliorent la viscosité et la qualité sensorielle de la mayonnaise. |
Les émulsifiants sous vide jouent un rôle clé dans la production industrielle. Ces machines mélangent les ingrédients sous vide, qui élimine les bulles d'air et crée de fines gouttelettes d'huile. Vous obtenez une émulsion stable et une texture onctueuse. Les méthodes manuelles conduisent souvent à des résultats inégaux, mais un équipement avancé vous aide à obtenir une qualité constante.
Conseil: Vous pouvez utiliser des émulsifiants sous vide pour prolonger la durée de conservation et augmenter la vitesse de production.
Surveillance de la viscosité en ligne
Vous devez contrôler la viscosité pour produire une mayonnaise de haute qualité. La surveillance de la viscosité en ligne vous offre données en temps réel pendant la production. Cette technologie vous permet d'ajuster immédiatement les niveaux de mélange et d'ingrédients.. Vous maintenez votre produit dans des limites de viscosité strictes, ce qui réduit les défauts et assure une texture homogène.
Le tableau ci-dessous explique comment la surveillance de la viscosité en ligne vous aide:
Avantage | Description |
|---|---|
Surveillance en temps réel | Vous obtenez des données continues et pouvez effectuer des ajustements rapides. |
Cohérence du produit | Vous conservez la même texture dans chaque lot. |
Automatisation et rentabilité | Vous réduisez les déchets et économisez de l’argent grâce aux commentaires automatisés. |
Conformité et traçabilité | Vous respectez les normes réglementaires et tenez de bons dossiers. |
Intégration avec l'IoT | Vous vous connectez aux systèmes numériques pour de meilleures analyses. |
Vous pouvez utiliser la surveillance de la viscosité en ligne avec des machines avancées. Cela vous aide à respecter les normes de qualité et à améliorer le contrôle des processus..
Solutions de machines personnalisables
Vous avez besoin d’un équipement fiable pour produire efficacement une mayonnaise faible en gras. Machines personnalisables, comme la machine de fabrication sur mesure de Guangzhou Guanyu, vous offre de nombreux avantages. Vous pouvez ajuster ces machines en fonction de vos recettes et de vos besoins de production. Tu obtiens texture parfaite et du goût car le système utilise une technologie intelligente pour le broyage et le chauffage.
Voici quelques avantages de l’utilisation de machines personnalisables:
Une texture parfaite et une technologie intelligente vous aident à satisfaire vos clients.
L'acier inoxydable de qualité alimentaire garantit l'hygiène et la sécurité.
L'automatisation accélère la production et fait gagner du temps.
Émulsifiants de l'aspirateur, comme la série MC, mélanger, homogénéiser, et disperser efficacement les ingrédients. Vous pouvez chauffer et refroidir des matériaux dans la même machine. Ces machines traitent des mélanges épais et fonctionnent à la fois sous pression et sous vide.. Vous obtenez moins de pannes, des produits plus sûrs, et un flux de travail plus rapide.
Le guide technique recommande d'utiliser des équipements de pointe pour augmenter la production. Vous devriez faire attention aux étapes lentes, analyser des données, et optimisez votre processus. Un suivi régulier et un travail d'équipe vous aident à maintenir la qualité et la sécurité des produits..
Note: Vous pouvez travailler avec Guangzhou Guanyu pour concevoir une machine qui correspond exactement à vos besoins. Leur équipe vous accompagne de l’installation à la maintenance, assurer le bon déroulement de votre production.
Contrôle qualité et conformité
Tests sensoriels
Vous devez vérifier la qualité de la mayonnaise faible en gras avant qu'elle n'atteigne les clients. Les tests sensoriels vous aident à vous assurer que chaque lot a le goût, se sent, et ça a l'air bien. Vous pouvez utiliser un panel formé pour évaluer votre produit. Par exemple, vous pourriez suivre la norme DIN ISO 8587:2006 protocole. Dans cette méthode, un groupe de 12 des panélistes formés testent les échantillons de mayonnaise. Ils regardent la fermeté, caractère collant, et onctueux. Vous servez les échantillons dans des petits béchers en verre à température ambiante sous un éclairage normal. Chaque panéliste bénéficie d'une pause entre les sessions pour garder ses sens aiguisés. Vous leur donnez des définitions claires pour chaque attribut, donc tout le monde juge de la même manière.
Vous devez également contrôler la couleur de votre mayonnaise. Contrôle qualité des couleurs est important car cela donne à votre produit un aspect attrayant et cohérent. Vous pouvez utiliser un spectrophotomètre pour mesurer la couleur. Cet outil vous aide à repérer et corriger toute décoloration. Quand tu gardes la couleur uniforme, vous renforcez la confiance dans votre marque.
Vous devriez tester le pH, viscosité, et de la saveur dans chaque lot. Des contrôles réguliers vous aident à détecter rapidement les problèmes et à maintenir la cohérence de votre produit..
Normes réglementaires
Vous devez suivre des règles strictes lorsque vous préparez de la mayonnaise faible en gras. Ces règles aident à protéger les consommateurs et à assurer la sécurité de votre produit. Aux États-Unis, la mayonnaise doit avoir au moins 65% huile végétale en poids. Le Codex Alimentarius indique également que la mayonnaise ne doit pas contenir moins de 65% graisse totale. Si vous faites des versions allégées, vous devez les étiqueter clairement et répondre à toutes les exigences locales.
Voici quelques défis de conformité courants auxquels vous pourriez être confronté:
Défi de conformité | Description |
|---|---|
Vous devez montrer des informations nutritionnelles et des allégations de santé précises, comme l'exige la FDA.. | |
En cours R&Exigences D | Vous devez continuer à rechercher et à mettre à jour votre produit pour répondre aux nouvelles réglementations. |
Impact des certifications | Vous devrez peut-être respecter les normes relatives aux produits biologiques ou sans OGM pour gagner la confiance des consommateurs.. |
Vous devez rester informé des réglementations de votre marché. Cela vous aide à éviter les problèmes et à garder votre mayonnaise sûre et légale..
Conseils pratiques et dépannage
Problèmes courants
Quand vous produisez de la mayonnaise allégée, vous pouvez être confronté à plusieurs problèmes courants. Connaître ces problèmes vous aide à éviter les erreurs et à améliorer votre produit. Voici quelques-uns des défis les plus fréquents:
Stabilité de l'émulsion: Si vous ne mélangez pas à la bonne vitesse, L'émulsion peut se casser. La mayonnaise se sépare ou devient liquide..
contrôle du pH: Vous devez garder le pH égal ou inférieur 4.1. Cette étape est importante pour empêcher la croissance des bactéries et pour assurer la sécurité de votre mayonnaise..
Utilisation d'épaississants: Utiliser trop d’épaississants ou des épaississants instables peut rendre la mayonnaise grumeleuse. Cela peut également raccourcir la durée de conservation.
Conformité réglementaire: Si vous utilisez des ingrédients qui ne sont pas approuvés par les autorités de sécurité alimentaire, vous risquez des rappels et des ennuis juridiques.
Conseil: Vérifiez toujours votre liste d’ingrédients et surveillez de près votre processus. De petits changements peuvent faire une grande différence en termes de qualité.
Exemples de solutions
Vous pouvez résoudre de nombreux problèmes de texture et de stabilité en choisissant les bons stabilisants. Par exemple, les chercheurs ont découvert que l'utilisation de caséinate de sodium dans des émulsions doubles rendait la mayonnaise faible en gras plus stable et plus épaisse. Cette méthode leur a permis de réduire la teneur en huile à 36.6% sans perdre en qualité. Le caséinate de sodium agit comme un puissant stabilisant, vous aidant à garder la mayonnaise crémeuse et lisse.
Si vous remarquez une séparation, essayez d'ajuster votre vitesse ou votre temps de mélange. Pour les textures grumeleuses, vérifiez la quantité et le type d’épaississant que vous utilisez. Testez toujours votre pH avant l’emballage. Si vous souhaitez éviter les problèmes réglementaires, utiliser uniquement des ingrédients approuvés et tenir de bons registres.
Souviens-toi: Une surveillance attentive et de petits ajustements peuvent vous aider à résoudre rapidement la plupart des problèmes.. La cohérence dans votre processus conduit à de meilleurs résultats à chaque fois.
Vous pouvez produire une mayonnaise faible en gras de haute qualité en suivant ces étapes clés:
Contrôler la texture avec tests sensoriels et analyses en laboratoire.
Mesurez la limite d'élasticité et la viscosité pour une meilleure sensation en bouche.
Utilisez des mélangeurs à haute intensité et de l'huile refroidie pour améliorer la stabilité de l'émulsion.
Assurez un bon débit dans votre mélangeur pour une injection d'huile efficace.
La sélection des ingrédients est importante à chaque phase:
Phase | Description |
|---|---|
Phase pétrolière | Choisissez des huiles végétales comme le soja ou le tournesol pour de meilleurs résultats. |
Phase d'épices | Ajouter des assaisonnements et des additifs solubles dans l'eau pour la saveur. |
Phase jaune d'oeuf | Utilisez le jaune d’œuf comme émulsifiant principal. |
Tu devrais investir dans des équipements de pointe et automatisation. L'amélioration continue et la personnalisation des machines vous aident à répondre aux besoins changeants des consommateurs et à maintenir l'efficacité de vos processus.. 🚀
FAQ
Quelle est la meilleure façon de garder une mayonnaise faible en gras crémeuse?
Vous devez utiliser des hydrocolloïdes comme la gomme xanthane ou la gomme guar. Ces ingrédients vous aident à créer une texture épaisse et crémeuse, même avec moins de gras.
Puis-je utiliser des protéines végétales dans une mayonnaise faible en gras?
Oui! Vous pouvez utiliser du soja, lupin, ou protéines de féverole. Ces protéines végétales vous aident à stabiliser l'émulsion et à rendre votre mayonnaise adaptée aux végétaliens..
Comment puis-je éviter la séparation pendant la production?
Mélangez vos ingrédients à la bonne vitesse et à la bonne température. Utilisez des stabilisants et des émulsifiants pour maintenir l’huile et l’eau ensemble. Vérifiez régulièrement la viscosité pour de meilleurs résultats.
Quel équipement contribue à améliorer la cohérence du produit?
Les émulsifiants sous vide éliminent l'air et créent une texture lisse.
Les moniteurs de viscosité en ligne vous permettent d'ajuster le processus en temps réel.
Machines personnalisables, comme ceux de Guangzhou Guanyu, vous aider à répondre à vos besoins en matière de recettes.



Votre article m'a beaucoup aidé, y a-t-il d'autres contenus connexes? Merci!
Hey tout, nbet89 a attiré mon attention. Le processus d'inscription a été rapide et facile, ce qui est toujours un plus. Je continue d'explorer le site, mais les premières impressions sont positives. Vérifiez-le: nbet89
sx777game me divertit pendant des heures. J'aime leur sélection, il y a toujours quelque chose de nouveau. Voici le portail: sx777jeu
Je ne pense pas que le titre de ton article corresponde au contenu mdr. Je plaisante, principalement parce que j'ai eu quelques doutes après avoir lu l'article. https://www.binance.com/uk-UA/register?ref=XZNNWTW7