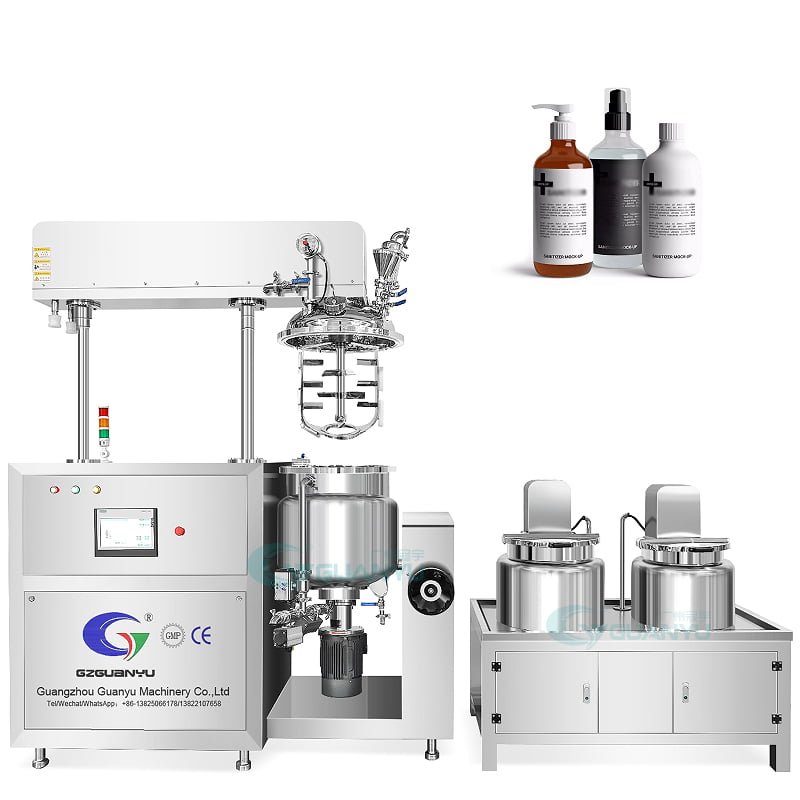
In the pharmaceutical industry, blending reactors, also known as mixing tanks or stirred vessels, are essential equipment for the mixing, dissolving, homogenizing, and heating/cooling of various liquids and semi-solid materials. This comprehensive article explores the types of pharmaceutical products that can be produced using mixing reactors and highlights the critical role they play in ensuring product quality and consistency.
Introduction to Blending Reactors
Mixing reactors are designed to facilitate the blending of ingredients under controlled conditions. They consist of a tank equipped with an agitator or stirrer that ensures thorough mixing of the contents. These reactors are versatile and can be adapted to various pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, from small-scale laboratory formulations to large-scale industrial production.

Types of Pharmaceutical Products Produced Using Blending machines
1. Solutions
Mixing reactors are extensively used in the production of pharmaceutical solutions. These include:
- Oral Solutions: Medications such as cough syrups and liquid vitamins.
- Injectable Solutions: Sterile solutions for injections, including vaccines and antibiotics.
- Topical Solutions: External applications like antiseptic solutions and eye drops.
Mixing reactors ensure the complete dissolution of active ingredients and excipients, resulting in clear and stable solutions.
2. Suspensions
Suspensions are liquid preparations containing finely divided, insoluble drug particles dispersed throughout a liquid phase. Common examples include:
- Antibiotic Suspensions: Used for oral administration, particularly in pediatric formulations.
- Antacid Suspensions: Liquids containing insoluble antacid particles.
Mixing reactors provide the high shear necessary to disperse and maintain the suspension of particles, preventing sedimentation and ensuring uniformity.
3. Emulsions
Emulsions are mixtures of two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, where one liquid is dispersed in the other. Examples of pharmaceutical emulsions include:
- Topical Creams and Lotions: Used for skin treatment.
- Oral Emulsions: Medications taken orally, like certain vitamins and nutrient supplements.
Mixing reactors facilitate the creation of stable emulsions by applying sufficient shear force to disperse one liquid phase into the other.
4. Ointments and Creams
Ointments and creams are semi-solid preparations used for external application. They include:
- Medicinal Ointments: Used for skin conditions, providing a barrier and delivering medication to the affected area.
- Cosmetic Creams: Moisturizers and anti-aging creams.
Mixing reactors ensure the homogeneous blending of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with the base materials, resulting in consistent and effective products.
5. Gels
Gels are semi-solid systems consisting of small molecules or particles dispersed in a liquid. They include:
- Ophthalmic Gels: Used for eye treatments, providing sustained drug release.
- Dermatological Gels: Used for skin conditions, delivering medication in a controlled manner.
- Oral Gels: Used for treating oral mucosal conditions.
Mixing reactors help in the uniform distribution of gel-forming agents and APIs, ensuring a smooth and consistent product.
6. Syrups
Syrups are concentrated aqueous solutions of sugar, often containing flavoring agents and APIs. They are commonly used in pediatric medicine due to their palatability. Examples include:
- Cold Syrups: Used for treating cough and cold symptoms.
- Vitamin Syrups: Nutritional supplements for children.
Mixing reactors are crucial in dissolving high concentrations of sugar and ensuring the even distribution of APIs and flavoring agents.
7. Injectable Solutions
Injectable solutions require strict sterility and homogeneity. They include:
- Vaccines: Used for immunization against various diseases.
- Antibiotic Injections: Used for treating severe infections.
Mixing reactors equipped with sterile components and precise control mechanisms ensure the production of safe and effective injectable solutions.
8. Topical Solutions
Topical solutions are applied to the skin or mucous membranes. They include:
- Antiseptic Solutions: Used for disinfecting wounds.
- Antifungal Solutions: Used for treating fungal infections.
Mixing reactors provide the necessary agitation and temperature control to produce stable and effective topical solutions.
9. Eye Drops
Eye drops are sterile solutions or suspensions for ocular use. They include:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: Used for treating bacterial eye infections.
- Lubricant Eye Drops: Used for relieving dry eye symptoms.
Mixing reactors ensure the sterility and homogeneity of eye drop formulations, which is critical for their safety and efficacy.
10. Nasal Sprays
Nasal sprays are liquid preparations intended for nasal administration. They include:
- Antihistamine Nasal Sprays: Used for treating allergic rhinitis.
- Decongestant Nasal Sprays: Used for relieving nasal congestion.
Mixing reactors facilitate the even distribution of APIs and excipients in nasal spray formulations, ensuring consistent dosing.
The Role of Blending Reactors in Pharmaceutical Production Processes
Mixing reactors play a pivotal role in various stages of pharmaceutical production. Their key functions include:
Effective Mixing and Homogenization
Mixing reactors ensure that all components are uniformly blended, preventing stratification and ensuring that each dose contains the correct amount of active ingredients. This is crucial for maintaining the therapeutic efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Temperature Control
Many pharmaceutical processes require precise temperature control. Mixing reactors can be equipped with heating and cooling systems to maintain the desired temperature range, which is essential for reactions, dissolutions, and maintaining the stability of heat-sensitive ingredients.

Sterility
Sterility is paramount in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly for injectables and ophthalmic products. Mixing reactors are designed to maintain sterile conditions, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring the production of safe and effective medications.
Scalability
Mixing reactors are adaptable to different production scales, from small-scale laboratory formulations to large-scale industrial batches. This scalability allows for consistent product quality and efficiency across various production volumes.
Process Optimization
Mixing reactors contribute to process optimization by reducing production times, minimizing waste, and improving yield. The controlled environment within the reactor allows for precise adjustments to optimize reaction conditions and enhance overall process efficiency.

Conclusion
Blending Reactors are indispensable in the pharmaceutical industry, providing essential capabilities for the production of a wide range of products, including solutions, suspensions, emulsions, ointments, gels, syrups, injectables, topical solutions, eye drops, and nasal sprays. Their ability to ensure effective mixing, precise temperature control, sterility, scalability, and process optimization makes them a critical component in pharmaceutical manufacturing. As technology advances, mixing reactors will continue to play a vital role in meeting the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the production of safe, effective, and high-quality medications.


Outstanding post but I was wanting to know if you
could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further.
Appreciate it!
My blog: nordvpn coupons inspiresensation
My partner and I stumbled over here from a different web page and thought I might as well check things out.
I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to checking out your
web page repeatedly.
my homepage; eharmony special coupon code 2025
The other day, while I was at work, my sister stole my apple ipad and tested to
see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views.
I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Review my blog post: Vpn
I’m not sure where you’re getting your info,
but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding
more. Thanks for excellent information I was looking for this info for my mission.
https://tinyurl.com/27xe7che gamefly 3 month free trial
It’s not my first time to pay a visit this web site,
i am visiting this site dailly and take nice
data from here every day. What does a vpn do https://tinyurl.com/2y95dtjr
Very descriptive blog, I loved that a lot. Will there be a part 2?
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post! It’s the little changes that will make the greatest changes.
Many thanks for sharing! Eharmony special coupon code
2025 https://tinyurl.com/yneylc4d
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading?
I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s
the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
my web page; http://winkler-martin.de/messages/61849.html
Magnificent goods from you, man. I have understand your
stuff previous to and you are just too wonderful. I really like what you have
acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still care for to
keep it smart. I can not wait to read much more from you.
This is actually a great website. vpn https://www.highlandguides.com
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.